China Leverages AI Advancements to Enhance Military Capabilities
In a groundbreaking development, researchers in the People’s Republic of China (PRC) have taken Meta’s open-source Llama model and optimized it for military and security applications. This new adaptation, called ChatBIT, has shown remarkable success in military demonstrations, particularly in areas like intelligence gathering, situational analysis, and mission support. Its performance surpasses other comparable models, raising considerable concerns regarding the implications of such innovations for global security.
Navigating Dual-Use Technologies
The surge in adopting open-source models like Llama for military purposes stems from their flexibility and potential for innovation. However, this also invites scrutiny over dual-use concerns. The adaptation of Llama by Chinese defense researchers underscores significant gaps in enforcing the restrictions associated with open-source technologies, leading to calls for stronger oversight measures. A notable voice in this conversation is Lieutenant General He Lei, former deputy director of the Academy of Military Sciences (AMS), who recently urged the United Nations to establish guidelines on artificial intelligence (AI) in warfare. While this suggests a desire to mitigate risks, China’s actions indicate a contrasting focus on leveraging AI to bolster its military capabilities.
Shifting Towards Intelligent Warfare
The PRC’s 2019 National Defense White Paper highlighted an ambitious vision for modern warfare—one that increasingly relies on advanced technology, including AI, for efficient command and operational execution. The military’s priority is to enhance battlefield situational awareness and enable agile decision-making through large AI models. This involves integrating diverse intelligence sources—from satellite imagery to real-time communications—into cohesive analyses that inform joint operations.
One area of application is cognitive and psychological warfare, where generative AI models are deployed to shape narratives and influence public perception, thereby undermining the morale of adversaries. Moreover, large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT prove invaluable in rapidly synthesizing and translating information, converting complex data into actionable insights to assist military personnel.
A Closer Look at Research Developments
Researchers are currently focused on refining the Llama model for the PLA’s specific needs. With the new release of Llama 3.1, boasting capabilities that rival elite proprietary models, adaptations from the Chinese military are surfacing. Innovations are ranging from high-quality code generation to sophisticated mathematical problem-solving, with specialized adjustments to address military contexts.
One of the key hurdles with Llama has been its reliance on general-purpose training data, which lacks necessary military context. To overcome this, PLA experts have initiated projects to construct domain-specific datasets and actively gather intelligence that better fits military requirements. They aim to enhance Llama’s performance in tasks crucial for defense, mastering Chinese-language military terminology and tactics through improved algorithms and advanced data collection methods.
Specialized Techniques for Optimization
Chinese researchers leverage strategies like Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for targeted enhancements without retraining entire models, ensuring efficient use of resources. Additionally, reinforcement learning techniques help fine-tune Llama’s outputs through iterative training sessions that improve responsiveness in military settings. These innovations not only maintain Llama’s core capabilities but also adapt it to highly nuanced military communication styles.
Expanding Applications of Llama-Driven Models
Emerging evidence suggests that Llama-based systems are being explored beyond military operations into areas such as predictive policing. The potential impacts of these models include improved situational awareness for law enforcement, enabling predictive analytics that prioritize responses to incidents. Pilot implementations are currently underway in regions like Yueqing, showcasing how data-driven insights can empower officers in the field.
In military scenarios, adaptations of Llama are being utilized for electronic warfare. For instance, simulations conducted by the Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC) reveal that the Llama model, in conjunction with reinforcement learning agents, improves strategies executed by units in the field by optimizing responses to evolving battlefield patterns.
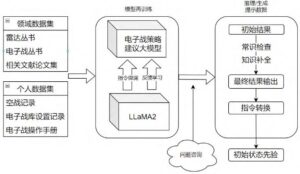
ChatBIT: The Future of Military Intelligence
Among the most promising developments is the ChatBIT model, derived from Llama, which specializes in military dialogue and open-source intelligence. Researchers report that ChatBIT outperforms other models, such as Stanford’s Vicuna-13B, on various military-specific benchmarks, demonstrating a strong capacity for understanding nuanced contexts and delivering accurate assessments.
For example, when queried about complex military metrics, ChatBIT provided detailed responses that significantly outperformed Vicuna-13B’s outputs. This capability highlights the model’s potential in supporting military Q&A and operational strategic analysis.
Conclusion: Striking a Balance
The integration of AI technologies like Llama into military applications raises profound questions about the ethical implications of dual-use technologies in global security. While Meta’s intentions behind releasing Llama as an open-source tool aligned with innovation ideals, the practical reality of its adaptation by the PLA raises red flags. The lack of effective enforcement of usage restrictions reflects a critical need for stronger regulations to safeguard against misuse.
As the PRC continues to refine and adapt AI technologies, the broader implications for international security cannot be ignored. Effective oversight is paramount to harnessing the benefits of such advancements while mitigating associated risks.
The AI Buzz Hub team is excited to see where these breakthroughs take us. Want to stay in the loop on all things AI? Subscribe to our newsletter or share this article with your fellow enthusiasts.