Enhancing Hydropower Cybersecurity with CYSAT-Hydro
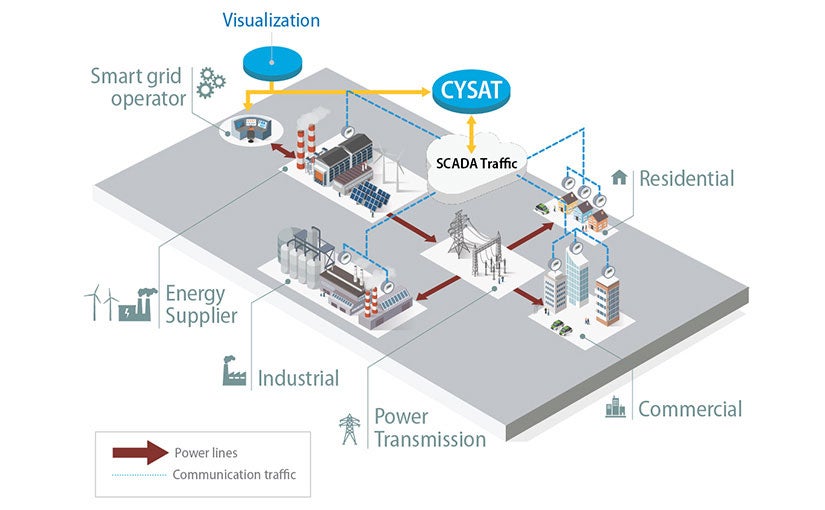
Diagram illustrating how the CYSAT-Hydro Tool communicates with the power grid. Illustration by NREL
The surge in internet-connected energy resources, coupled with recent cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure, has triggered significant concerns regarding the cybersecurity of the United States power grid. To address these vulnerabilities, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) is in the process of developing an innovative tool aimed at improving the cybersecurity of hydropower plants: the Cybersecurity Situational Awareness Tool for Hydropower (CYSAT-Hydro).
What is CYSAT-Hydro?
CYSAT-Hydro is a sophisticated, data-centric cybersecurity solution that utilizes artificial intelligence (AI) to identify and respond to potential cyber threats. This tool is specifically designed to safeguard the digital touchpoints of hydropower facilities from emerging cyber risks, thereby bolstering the overall reliability of the power grid. Development of CYSAT-Hydro is supported by the US Department of Energy’s Water Power Technologies Office.
As hydropower facilities increasingly adopt smart grid technologies, including battery energy storage systems and sophisticated communication infrastructures, new vulnerabilities are being introduced. These technologies enhance the reliability of the grid, but they also enlarge the attack surface for cybercriminals. The significant economic ramifications of cyber threats were starkly illustrated by the ransomware attack on the Colonial Pipeline in May 2021, which led to substantial financial losses and widespread fuel supply disruptions.
Insights from Cybersecurity Experts
Vivek Kumar Singh, a senior cybersecurity researcher at NREL and a key member of the CYSAT-Hydro development team, emphasized the growing trend of adversarial attacks on critical infrastructure. “In the last 10 to 15 years, there has been an observable rise in malicious activities from both independent and nation-sponsored actors targeting vital components of infrastructure like the power grid due to their potential for considerable impact and financial gain,” he stated.
How CYSAT-Hydro Strengthens Cyber Defense
CYSAT-Hydro employs AI to continuously monitor the operational technology networks of hydropower plants, detecting any anomalies that may signal a cyber intrusion. Upon identifying an anomaly, the tool offers comprehensive insights to system operators, enabling them to promptly grasp the nature of the threat and respond effectively. This real-time analytical capability is critical for sustaining grid operations during and after a cyber event.
In addition to securing against cyber threats, CYSAT-Hydro calculates technical and economic performance metrics for various distributed energy resources. These evaluations assist grid operators in understanding the possible financial repercussions of a cyberattack, thereby aiding in more informed decision-making.
Singh highlighted the substantial costs associated with cyber incidents, stating, “Consider the duration of a cyberattack and the potential losses for operators. An attack that shuts down a hydropower facility for just five hours could result in immense financial implications while also affecting flood control, local water supplies, and ecosystems. This tool could play a pivotal role in preventing such disruptions.”
Accessibility and Future Development
CYSAT-Hydro is set to be launched as an open-source tool, encouraging widespread adoption across different grid technologies and critical infrastructure sectors, including water and gas pipelines. It features a user-friendly interface compatible with various operating systems and offers a real-time visualization dashboard, providing an all-encompassing view of grid operations, network traffic, and possible intrusions.
“This tool is fundamentally data-oriented,” Singh explained. “If you have insights into past cyberattacks—specifically where they occurred—you can apply this tool to other supervisory control and data acquisition systems beyond just hydropower facilities.”
As CYSAT-Hydro approaches its final development stages, NREL is actively seeking industry partnerships to test the tool in real-world settings and to explore its commercial potential. Singh and his team are also focused on conducting additional case studies to refine the tool’s functionality further.
“We are keen on field testing and exploring technology commercialization in conjunction with industry partners and utility providers. Additionally, we plan to continue enhancing this tool through case studies to boost its effectiveness,” Singh concluded. “As we prepare to submit our final report to the Water Power Technologies Office, we will also consider future advancements for CYSAT-Hydro to enhance cybersecurity across clean energy systems.”
Based on a report by Tim Meehan.